
Механики XXI веку. №15 2016 г.
222
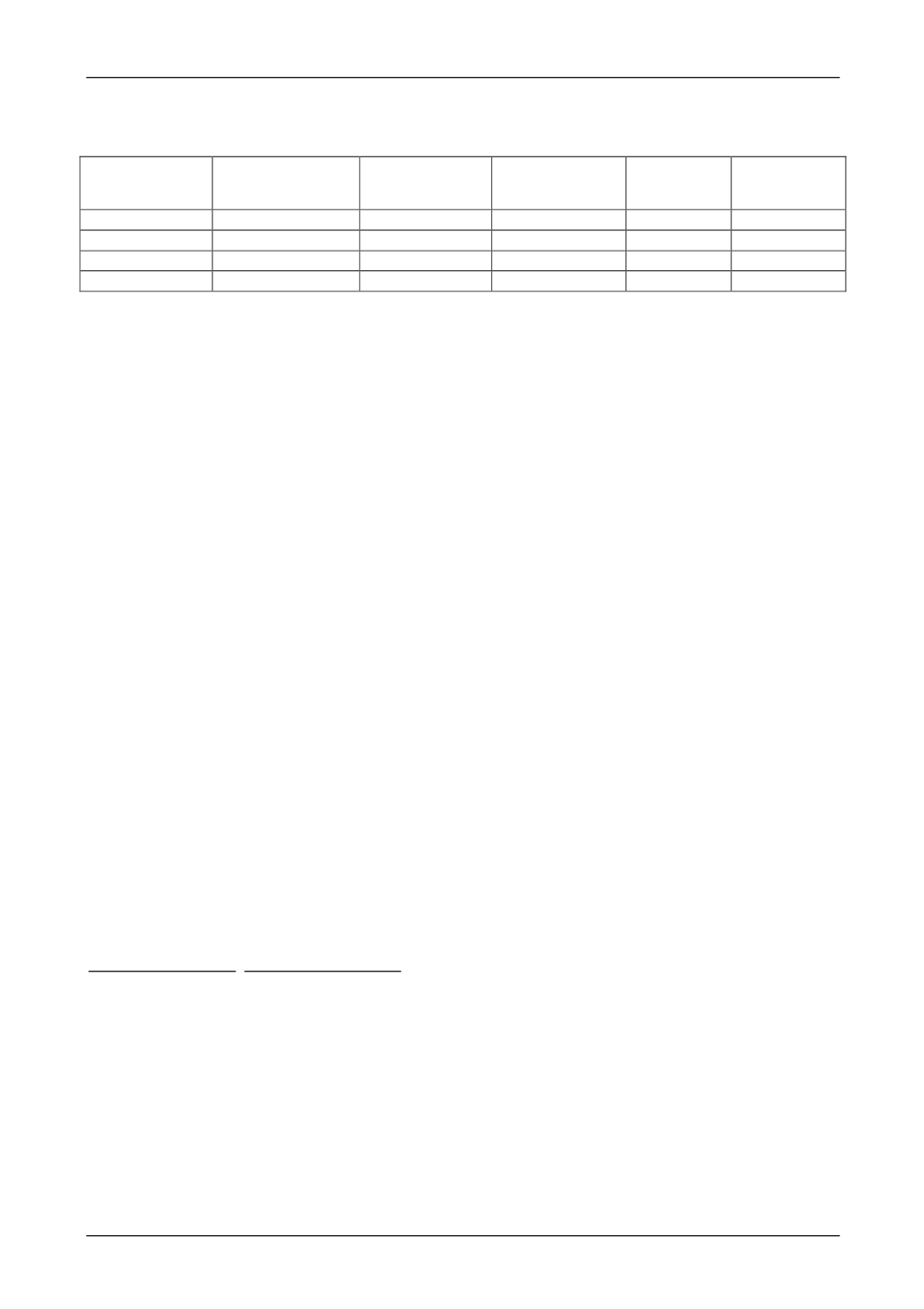
Таблица 1.
Результаты расчета длины микротрещин и минимальной относительной площади неповрежденного
трещиной сечения элементарной ячейки накануне слияния соседних трещин при условии
t
u
01,0
Материал
Па
t
11
10,
расчет.
Па
u
9
10,
расчет.
Па
u
9
10,
[22]
м l
cr
6
10,
,
4
10
Al
0,07
0,07
0,05
15
0,84
Cr
0,37
0,37
0,41
17
1,05
Ti
0,21
0,21
0,24
17
1,07
Mo
0,53
0,53
0,80
7
1,23
Литература:
1. Griffith A. A. The phenomena of rupture and flow in solids // Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London. Ser. A. 1920.
Vol. 221.P. 163 – 198.
2. Райзер Ю. П. Физические основы теории трещин хрупкого разрушения // Успехи физических наук.
1970. Т. 100. Вып. 2.С. 329 – 347.
3. Xi-Qiao Feng, Shou-Wem-Yu. Damage Micromechanics for Constitutive Relations and Failure of
Microcraced Quasi-Brittle Materials // International Journal of Damage Mechanics. 2010. Vol. 19, 8. P. 911 – 948.
4. J. Li, X. B. Zhang. A Unified Failure Criterion for Brittle or Quasi-Brittle Materials under Arbitrary Stress
Concentration // Fracture of Nanj and Engineering Materials and Structures. 2006.P. 1119 – 1120.
5. Петч Н. Металлографические аспекты разрушения / Ред. Г. Либовиц // Разрушение. – М.: Мир, 1973.
Т. 1. Микроскопические и макроскопические основы механики разрушения. С. 376 – 420.
6. Рыбин В. В. Большие пластические деформации и разрушение материалов. М.: Металлургия, 1986.
244 с.
7. Бусов В. Л. Рассеяние ультразвуковых волн на микротрещинах в фрагментированных
поликристаллах // Акустичний вiстник. 2007. T. 10. № 3. С. 19 – 24.
8. Волынский А. Л., Ярышева Л. М., Моисеева С. В., Баженов С. М., Бакеев Н. Ф. Новый подход к
оценке механических свойств твердых тел экстремально малых и больших размеров // Российский химический
журнал. Журнал Российского химического общества им. Д. И. Менделеева. 2006. Т. 50. № 5.С. 126 – 133.
9. Панин В. Е., Егорушкин В. Е. Физическая мезомеханика и неравновесная термодинамика как
методологическая основа наноматериаловедения // Физическая мезомеханика. 2009. Т. 12. № 4. С. 7 – 26.
10. Сарафанов Г. Ф., Переверзенцев В. Н. Зарождение микротрещин в фрагментированной структуре //
Вестник Нижегородского университета им. Н. И. Лобачевского. Исследования физической природы
фрагментации материалов.2010.№ 5 (2). С. 90 – 94.
11. Francois Hild, Pascal Forquin, Christophe Ltnoual and Xvier Brajer. Probalistic-deterministic transition
involved in a fragmentation process of brittle materials: application tu a high performance concepte // Latin American
Journal of Solids and Structures.2005.№ 2.P. 41 – 56.
12. Zhu T. T., Bushby A. J. and Dunstan D. J. Materials mechanical size effects: a review // Materials
Technology. 2008.Vol. 23.№ 4.P. 193 – 209.
13. Физические величины [Текст]: Справочник / А. П. Бабичев, Н. А. Бабушкина, А. М. Братковский и
др. под ред. И. С. Григорьева, Е. З. Мейлихова. – М.: Энергоатомиздат, 1991.1232 с.
Durability laminates
Presnetsova V.Y., Romashin S.N., Frolenkova L.J., Shorkin V.S., Yakushina S.I.
Prioksky State University
,
302020, Naugorskoe shosse, 29,Orel, Russian Federation
VShorkin@yandex.ru,Jakushina@rambler.ru
Keywords:
laminates materials, the theoretical tensile strength, the actual breaking stress.
The theoretical strength of a perfect crystal lattice, which corresponds to the simultaneous breaking of
intermolecular bonds, is very high - only ten times less than the Young's modulus. Strength of real solids is several
orders of magnitude smaller. This is linked with the existence of lattice defects. In the work of the various types of
defects are considered only crack. Although really brittle materials is very small. Question of cracks in brittle solids is
of great practical importance because many plastic materials (metals) are destroyed "brittle" manner. Problem of
brittle fracture paid much attention. Trying to explain the discrepancy between the actual and theoretical values of
strength in the presence of cracks was made by Griffith in his theory of brittle fracture of amorphous materials. He
suggested that the real materials have a large number of small cracks, which can act as stress concentrators,
increasing their value to the theoretical strength. The process reduces the gap while increasing the length of cracks
until complete separation of the sample into two parts.














